Understand Hair science and biology
Hair is much more complicated than it looks. It can be felt at the root when it’s moved or pulled. It protects the skin and traps particles like dust around eyes and ears. If hair gets damaged, it can renew itself without scarring. Hair covers almost every surface of the human body. It not only plays a vital role in the appearance of both men and women, but it also helps to transmit sensory information as well as create gender identification. Lets get important facts about hair structure, science & different parts of hair.
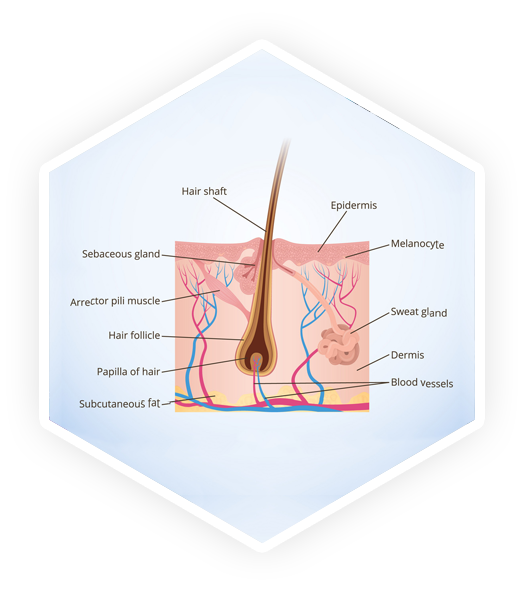

Hair Anatomy
What is hair made up of?
Hair is made up of 95% keratin, a tough protein, shaped like a helix that forms the strength of the skin and all its appendages (body hair, nails, etc.). Keratin is a large molecule made up of smaller units called amino acids.
How many hair approximately scalp contain?
The human scalp contains approximately 100,000 to 150,000 hair follicles. Since follicles do not continue to grow during life, this is the largest number of hair a human will ever have. In fact, as we get older, the number of hair follicles per square inch decreases as our bodies stretch and grow.
What is natural hair density on scalp in cm2?
A full, healthy head will typically contain 70-120 hairs per cm2. It may vary from person to person and ethnicity due to several factors like thickness, texture, length and color. Hair density from 50-80/cm2 is often unnoticed and density below 50/cm2 is considered to be noticeably thinning hair. Your hair density is usually highest at crown.
Structure of hair
Hair is made up of different separate structures. In simple language we can understand it by dividing hair in two parts – below the skin and above your skin. The hair follicle is the part below the skin, and the hair shaft is what you see above your skin. Hair follicle sits above a dermal papilla.

Dermal Papilla
The dermal papilla induces the development of hair follicles in the fetus and appears to play an important role in follicular cycling and hair growth as it have collection of mesenchymal tissue with inductive properties. It nourishes the hair root to keep it growing.

Hair follicle
The hair follicle is the point from which the hair grows. It anchors each hair into the skin. It's a stocking-like structure that starts in the epidermis, the skin's top layer. It extends to the dermis, second layer of skin. Hair follicles consist of four segments: the bulb, suprabulbar region, isthmus, and infundibulum.
- The bulb, the lowest portion (base) of the hair follicle, is the site of the hair matrix, a group of rapidly proliferating cells responsible for the production of hair. Hair bulb is where the hair gets nourishment, hormones that modify growth and pigment that provide color.
- The follicle is lined by inner and outer layers that protects and molds the growing hair. The oil gland or sebaceous gland opens in the inner layer. This gland produces oil or sebum which is body's natural conditioner. A muscle called erector pili is attached to the outer layer, when the muscle contracts the hair stand ups called as goosebumps.

Hair shaft
The hair shaft is the part of the hair that we can see. Once the hair grows beyond the skin's surface, the cells aren't alive anymore. The hair shaft is made of a hard protein called keratin and is made in three layers. Those layers are:
- The Inner Layer: This is called the medulla. Depending on the type of hair, the medulla isn't always present.
- The Middle Layer: This is called the cortex, which makes up the majority of the hair shaft. Both the medulla and the cortex contain pigmenting cells that are responsible for giving hair color.
- The Outer Layer: This is called the cuticle, which is formed by tightly packed scales in an overlapping structure that resemble roof shingles. Many hair-conditioning products are formulated to even out the cuticle by smoothing out its structure.

Hair Bulge
It is a region near the insertion of the arrector pili muscle, referred to as the bulge region of the hair follicle. It harbors hair follicle stem cells that are essential for follicular cycling and hair growth. The loss of the hair follicle stem cells in the bulge is postulated to contribute to permanent loss of hair in cicatricial alopecias.
Is white part at end of hair is root ?
No, it is not root. That white bulb at end of falling hair or plucked hair is protein bulb. Hair with white bulb is called club hair and this white part is responsible for rooting the hair in follicle till it grows healthily.
Will hair with white bulb grow back ?
It’s a myth that hair with white bulb will not grow back. It’s just a protein sheath, not hair root. So you should not worry about it.
Hair Types
The two major types of hair follicles on the human body are terminal hair follicles and vellus hair follicles.
Features | Terminal hair | Vellus hair |
Depth | Subcutaneous fat (2 to 5 mm from skin surface) | Reticular Dermis |
Thickness | 0.06 mm | 0.03 mm |
Sites | Scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, underarms, pubic area | Remaining areas |
Color In Indians | Darker (Black or dark brown) | Lighter (Brown) |
In underarms & genital areas conversion of vellus hair to terminal hair is part of physiological development during puberty. Transitioning between terminal and vellus hair follicles may also occur in pathologic states. Abnormal transitioning of vellus hairs to terminal hairs occurs in hirsutism in women, and transitioning of terminal hairs to vellus hairs (follicular miniaturization) is a classic feature of androgenetic alopecia.
The term “intermediate hairs” has been used to describe hairs with characteristics that are between vellus and terminal hairs (0.03 to 0.06 mm)






